Buffer Ib Chemistry Definition
Buffer definition is - fellow man. A buffer consists of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid.
 Rate Of A Chemical Reaction Chemical Kinetics Chemical Kinetics Chemical Reactions University Chemistry
Rate Of A Chemical Reaction Chemical Kinetics Chemical Kinetics Chemical Reactions University Chemistry
A lot of biological and chemical reactions need a constant pH for the reaction to proceed.

Buffer ib chemistry definition. For names of specific solutions see under the name. Its pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it and is thus used to prevent a solution s pH change. A buffer solution can be made by mixing a weak acid with one of its salts OR mixing a weak base with one of its salts.
Acidic solutions contain high concentrations of hydrogen ions H and have pH values less. It is able to neutralize small amounts of added acid or base thus maintaining the pH of the solution relatively stable. In pharmacology a liquid preparation of one or more soluble chemical substances which are usually dissolved in water.
The buffer capacity is a quantity in resisting the pH change at the time of addition of an acid or base. A buffer is an aqueous solution that consists of a mixture of a weak acid and its salt acid buffer or a weak base with its salt basic buffer. It is able to neutralize small amounts of added acid or base thus maintaining the pH of the solution relatively stable.
A buffer is a solution that can maintain a nearly constant pH if it is diluted or if relatively small amounts of strong acids or bases are added. Buffers are used to maintain a stable pH in a solution because they can neutralize small amounts of additional base acid. March 26 2018 Here we are going to learn about buffer capacity chemistry definition and formula.
This is important for processes andor reactions which require specific and stable pH ranges. A buffer is a solution that can resist pH change upon the addition of an acidic or basic components. Buffer capacity β is defined as the moles of an acid or base necessary to change the pH of a solution by 1 divided by the pH change and the volume of buffer in liters.
If you add an acid or a base to a buffered solution its pH will not change significantly. A buffer is a solution that can resist pH change upon the addition of an acidic or basic components. Buffers are solutions that resist a change in pH on dilution or on addition of small amounts of acids or alkali.
In other words a buffer is an aqueous solution of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. The higher the acid concentration of the buffer then the buffer capacity will be higher as well. Buffers are used to make solutions of known pH especially for instrument calibration purposes.
Buffer chemistry synonyms Buffer chemistry pronunciation Buffer chemistry translation English dictionary definition of Buffer chemistry. From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia A buffer solution more precisely pH buffer or hydrogen ion buffer is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or vice versa. Buffer in chemistry solution usually containing an acid and a base or a salt that tends to maintain a constant hydrogen ion concentration.
A buffer is an aqueous solution that has a highly stable pH. How are Acid-Base Buffers Made. Its pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it.
An example of a common buffer is a solution of acetic acid CH 3 COOH and sodium acetate. It is a unitless number. 005of a weak acid and its conjugate base.
By definition a buffer system is a solution that resists a change in pH when acids or bases are added. Buffer capacity is the amount of acid or base that can be added before the pH of a buffer changes. Buffer bŭf ər Chemistry A substance that prevents change in the acidity of a solution when an acid or base is added to the solution or when the solution is diluted.
A homogeneous mixture of one or more substances solutes dispersed molecularly in a sufficient quantity of dissolving medium solvent. How to use buffer in a sentence. A solution which can maintain an almost constant pH value when dilute acids or alkalis are added to it.
A buffer resists changes in pH due to the addition of an acid or base though consumption of the buffer. This does not mean that the pH of buffers does not change. A buffer is an aqueous solution used to keep the pH of a solution nearly constant.
A buffering agent is a weak acid or weak base that helps maintain the pH of an aqueous solution after adding another acid or base. Ions are atoms or molecules that have lost or gained one or more electrons. Buffers are extremely useful in these systems to maintain the pH at a constant value.
This is important for processes andor reactions which require specific and stable pH ranges.
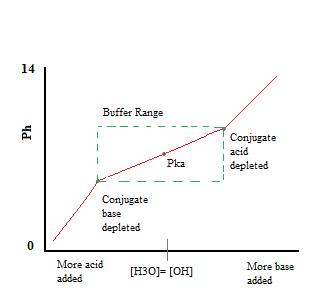 Introduction To Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
Introduction To Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
 18 3 Buffer Solutions Hl Youtube
18 3 Buffer Solutions Hl Youtube
 Buffer Solutions A Guide For A Level Students Ppt Download
Buffer Solutions A Guide For A Level Students Ppt Download
 Bahahhaha This Is My Fave Biology Humor Chemistry Jokes Chemistry Puns
Bahahhaha This Is My Fave Biology Humor Chemistry Jokes Chemistry Puns
 Buffer Solution Acidic Buffer Basic Buffer Animation Buffer Solution Electron Configuration Solutions
Buffer Solution Acidic Buffer Basic Buffer Animation Buffer Solution Electron Configuration Solutions
 Acids Bases Draw It To Know It Chemistry Education Study Chemistry Biochemistry Notes
Acids Bases Draw It To Know It Chemistry Education Study Chemistry Biochemistry Notes
 Buffer Solution Preparation Of Buffer Solution Acidic Basic Buffer Buffer Action Buffer Solution Solutions Electron Configuration
Buffer Solution Preparation Of Buffer Solution Acidic Basic Buffer Buffer Action Buffer Solution Solutions Electron Configuration
 Buffer Solutions How To Solve Ib Chemistry Problems In Hl Paper 1 Part 34 Youtube
Buffer Solutions How To Solve Ib Chemistry Problems In Hl Paper 1 Part 34 Youtube
 What Is A Biological Buffer And How To Choose The Best Buffer For Your Experiment Goldbio
What Is A Biological Buffer And How To Choose The Best Buffer For Your Experiment Goldbio
 Buffer Solutions Buffer Solution Fun Learning Ap Chemistry
Buffer Solutions Buffer Solution Fun Learning Ap Chemistry
 Buffer Solution Preparation Of Buffer Solution Acidic Basic Buffer Buffer Action Buffer Solution Electron Configuration Solutions
Buffer Solution Preparation Of Buffer Solution Acidic Basic Buffer Buffer Action Buffer Solution Electron Configuration Solutions
 17 2 Buffer Solutions Chemistry Libretexts
17 2 Buffer Solutions Chemistry Libretexts
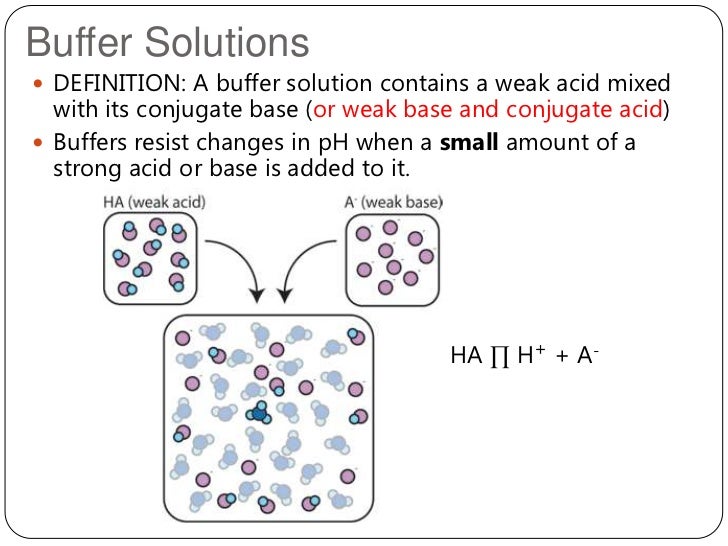 2012 Topic 18 2 Buffer Solutions
2012 Topic 18 2 Buffer Solutions
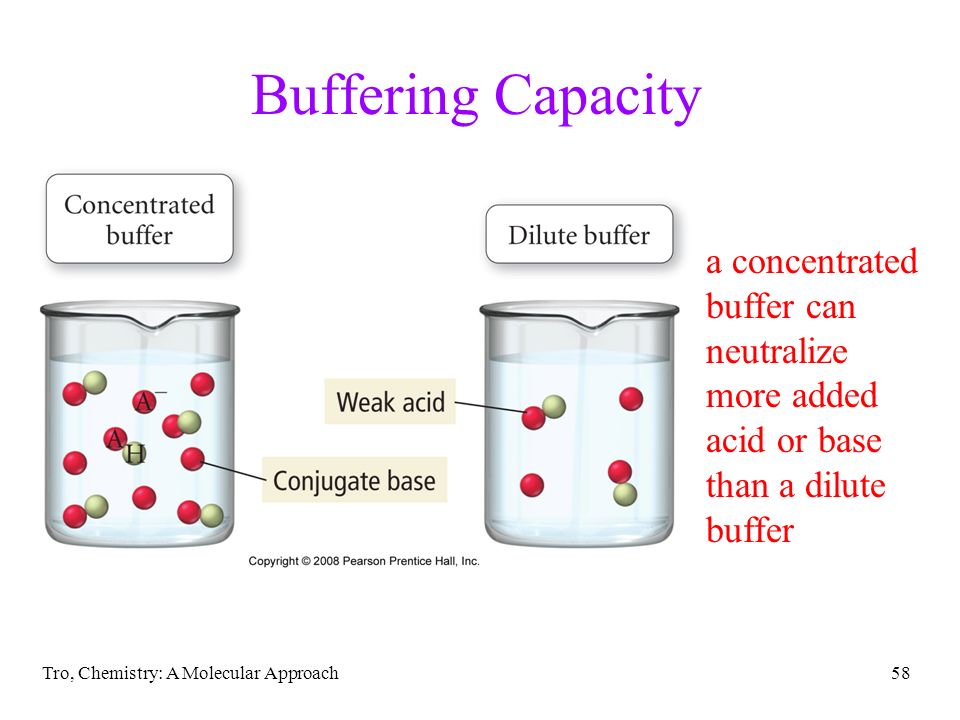 Chapter 16 Aqueous Ionic Equilibrium Ppt Download
Chapter 16 Aqueous Ionic Equilibrium Ppt Download




